|
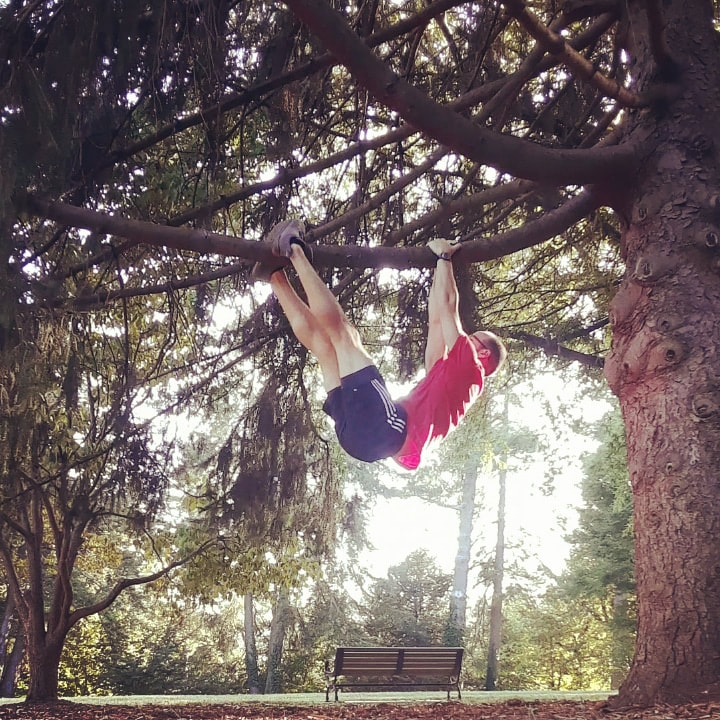
Guest Blogger: Kai Leathers Who Are We?Many Buddhist traditions claim that there is no "self". That is an esoteric topic for another time, but I believe they are right in more ways than one. Modern science is (re)discovering that we are not just a single biological entity; instead, we must think of ourselves as a superorganism. This may sound like the beginning of a horror movie, but it is actually as mundane as a teaspoon of soil in your backyard (which averages between 100 million and 1 billion bacteria). It is quickly becoming common knowledge that humans cannot survive without a thriving diversity of microorganisms. Even if you have not spent any significant amount of time in the world of holistic health or nutrition, you have probably heard the term "microbiome". Tons of research is revealing that we are not just Homo sapiens ("wise man"), but instead we are host to a huge collection of bacteria, viruses, protozoa, yeast and other fungi that scientists call the microbiome. Indeed, we are never alone. They live on and inside of us, and their lives are essential to the proper functioning of our body systems. In order to optimize health, we must not feed our singular selves, but we must instead feed our collective "superorganism" community - these microscopic colonies in our intestines, or gut. Globally, we are undergoing a sixth major extinction period, and some who study the human microbiome believe our gut bacteria are experiencing a similar extinction. They hypothesize that we may never be able to replace certain bacterial strains that we have lost. Exercise and Gut HealthYou may have cornered a stranger at a dinner party to explain the TED talk you recently watched, discussing ways to increase the diversity of your gut bacteria by changing your diet, but have you heard about how exercise also affects your gut microbiome? Researchers from Rutgers University and University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign are showing that exercise also has an impact on the amount and type of bacteria in our gut. Experiments have been carried out on mice and humans. One human study looked at previously sedentary lean and obese individuals, and after 6 weeks of supervised cardiovascular exercise lasting a half our to an hour in duration, the composition of their gut microbiomes changed. Certain kinds of bacteria that produce a short chain fatty acid called butyrate, which is associated with positive gut health, increased in number. There was a difference between the concentrations of butyrate-producing bacteria in lean participants in comparison to the obese participants, so there is still more research to be done. These levels of bacteria also decreased after the participants returned to a sedentary lifestyle 6 weeks later, further establishing the link between exercise and the growth of positive species of bacteria. There are many mechanisms that may contribute to the increase in butyrate-producing bacteria, but scientists are still not sure why the change takes place. This is one area where more research is being done. Possible mechanisms include altered gene expression of immune cells in gut tissue, changing the mucus composition of the gut, raising the core body temperature, which results in less blood flow to the intestines, or increasing the activity of bile acids and lactate levels. Keep It SimpleNow that we have another reason to get moving, how do we incorporate this into our practice? A few times a week, you should try to really push your heart rate. Most people might turn to running or cycling, but you can turn any exercise into a "cardio" exercise. One of the most underrated ways to increase your aerobic activity is getting up and down from the ground. In the video below, I demonstrate a MovNat-inspired exercise that is amazing in many ways. This exercise is particularly useful for establishing proprioception, balance, core strength, shoulder stability, and hip mobility. It is the essence of "functional" movement in my eyes because it can increase your athletic skill, or it can simply help you be more efficient at getting up from the ground. Start on your back, then sit up and place one hand right next to your hip and pull the opposite heel in close to your butt. Lift your butt of the ground and pull the free knee under you as you come into a tripod position with your two feet and one hand. Push yourself to standing, then reverse the order to return to the ground. Once you master the movement try adding in a kick through or jumps into the transition, as seen in the video below. You will be surprised at how quickly your heart rate can spike after just a few reps of this exercise. Try throwing in 5 minutes of this exercise in the middle or your normal cardio routine. For example, if you run, run for 10 minutes, then try a get-up for 5 minutes before going back into your run. You can also put this on the beginning of your run for a 5 minute warm-up or throw it on the end of your run for a 5 minute finisher to spike your heart rate before a cool-down and stretch. Insta: move.with.kai blog: https://kaileatherswellness.gator.site/blog/move.with.kai Sources:
hsph.harvard.edu/nutritionsource/microbiome/ https://journals.lww.com/acsm-msse/fulltext/2018/04000/Exercise_Alters_Gut_Microbiota_Composition_and.14.aspx https://www.the-scientist.com/news-opinion/exercise-changes-our-gut-microbes--but-how-isnt-yet-clear-66281 http://nautil.us/issue/30/identity/how-the-western-diet-has-derailed-our-evolution |
Eileen Brantley & Amy WrightWe are Herb Girls Athens, LLC. Read our blog! Archives
November 2022
Categories
All
|

 RSS Feed
RSS Feed
